Blockchain is a technology that, when applied to logistics, has a major impact on traceability and other aspects of the supply chain.
Blockchain is a decentralized way to share information in a safe and trustworthy manner thanks to its system of block chains validated in consensus. This means that every block of data is shared among several agents that validate it and guarantee its inviolability without the need of an intercessor to consolidate the information.
Blockchain records every information exchange or coded transaction simultaneously in the copies of each of the agents involved in the verification; therefore, information cannot be independently changed once it has been recorded.
Blockchain’s was used first as the shared database of Bitcoin, the cryptocurrency launched in 2008, but people soon realized its usefulness for other applications.
Applied to logistics, for example, it lets you record and authenticate the barcodes of products along the supply chain so you can monitor merchandise in real time; in this way, anyone involved in the blockchain can detect immediately if there is any attempt to modify or falsify the data of products or orders.
This image shows in detail how blockchain works and its relationship with the supply chain:
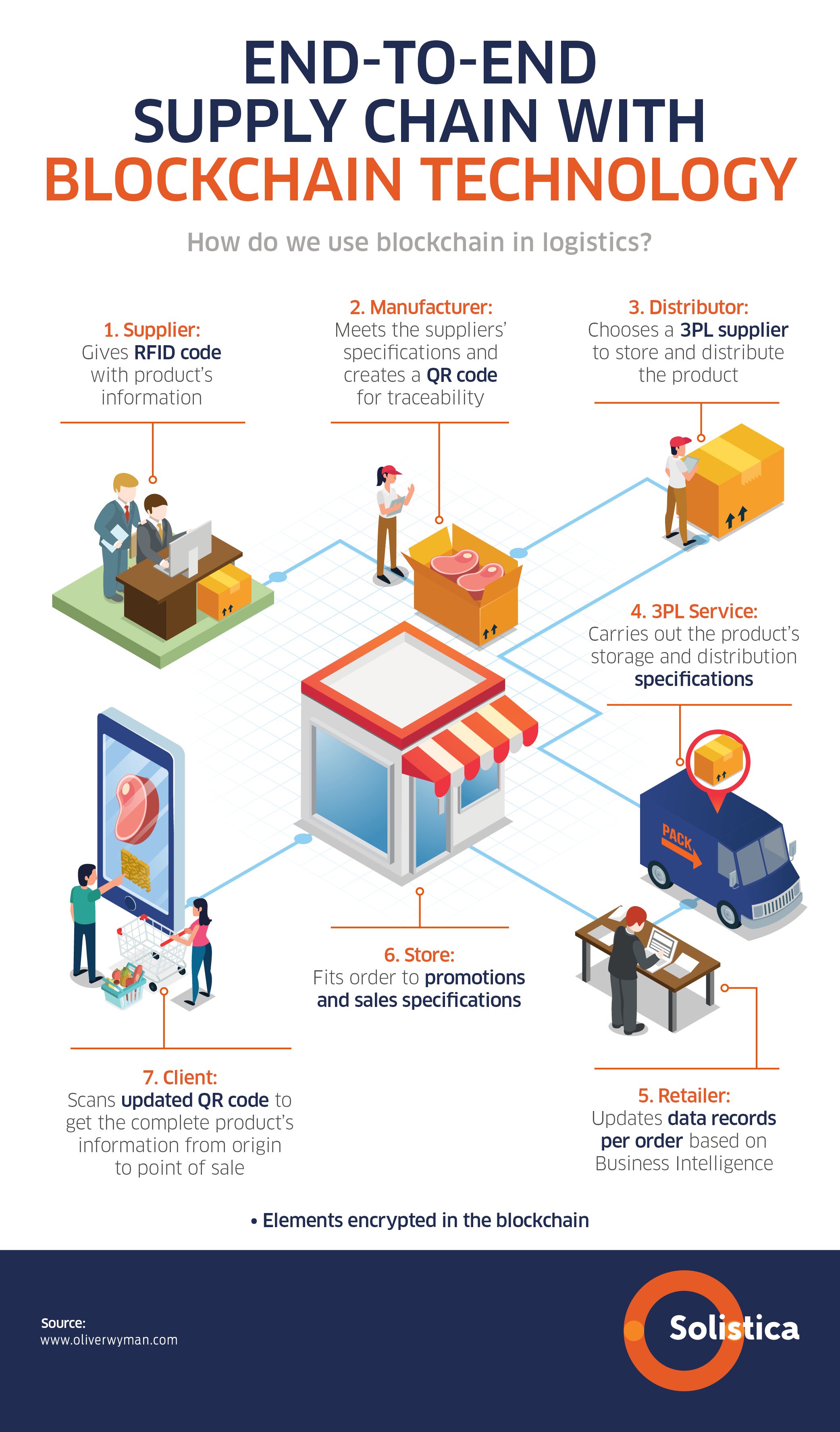
Blockchain and logistics
Going deeper into its uses in logistics, the blockchain has been designed to provide solutions for the complex ecosystems of the logistics chain where there is not a main participant, where collaboration among those involved sometimes is not trustworthy, where information must be centralized, and where the safety of said information is of top priority. By using blockchain in logistics we can make an alliance between these ecosystems to foster the necessary trust among all the collaborators in the chain, either partners or competitors, guaranteeing the protection, traceability, and confidentiality of processes.
Blockchain offers visibility from A to Z when it comes to sending goods; every event related to certain product (either during manufacturing, processing, transport, storage, or delivery) is recorded as a blockchain transaction, monitoring also the documentation and packaging associated with said product.
Using a platform with this technology in logistics guarantees that:
- The coordination of the necessary documents to identify and validate the cargo gets easier and safer, reducing the paperwork.
- We can enter into “smart contracts” whose validity and fulfillment we can verify in real time, making imports and exports procedures quicker and more efficient.
- The data exchanged between the logistics actors is trustworthy; this, in turn, allows for timely and accurate decision making when it comes to expediting the transit of merchandise through warehouses and customs.
- The system offers scalability, resulting in immediate solutions as the demand of fast order deliveries increase.
- The trust generated by the truthfulness of the information eliminates the need for constant audits to confirm it.
In short, all this helps eliminate the bureaucratic processes, the long waiting periods, and, therefore, the hindering of the merchandise flow.
Together, technology and consulting giant IBM and Danish transport company Maersk are using this technology in unison to expedite the information flow and financial transactions and to lower the time spent in bureaucratic procedures along their logistics processes.
According to research carried out by Maersk in 2014 and referenced by IBM in the announcement of its Hyperkedger Fabric system in 2017, generally, transferring refrigerated products from Africa to Europe demands the participation of some 30 companies or agents and represents the creation of 200 documents to support the interactions. Both companies, leaders in their own sectors, expect to lower times and costs significantly by using blockchain technology.
In Rotterdam, the largest port in the Netherlands and Europe, over 15 public and private companies created a consortium two years ago to begin experimenting with blockchain technology. They aim to test its application on logistics and have found so far increasing benefits when integrated to the Internet of Things (IoT) and modern supply chain management systems.
Benefits of using this technology
According to Germán Sánchez Couso, consultant of Blockchain and Business Transformation at IBM Spain, the ease in which we can record what is going on in every step of the supply chain guarantees the traceability of merchandise.
The most noticeable attribute of the blockchain technology in this sense is that once the information has been stored, it cannot be changed, this helps people trust the rules have been followed and that there is a trustworthy way to monitor the entire distribution flow or just
The following are some of the advantages of using blockchain technology in logistics processes:
- Saving time and costs in supply chain management by reducing paperwork.
- Eradicating mistakes and fraud.
- Optimizing the storage, transport, and distribution processes.
- Offering reliability and integrity of shared information.
- Fostering an efficient collaboration between the different parties involved.
- Offering transparency along the merchandise flow so clients can always know where their orders are.
- Offering improved cargo safety because the consensus validation of the information lets us know if someone wants to commit fraud by altering a record code.
Each of these benefits of using blockchain technology in the supply chain will result in a better customer service and better profitability for your business.
Future challenges
Integrating blockchain technology in the supply chain translates into process agility, information safety and veracity, process transparency, and collaboration trust. All these, in the end, will result in lower costs, logistics efficiency, and improved profitability for your business.
Even though blockchain implementation has been limited so far, we expect a rapid growth in the adoption of this technology in the next years and of BiTA (Blockchain in Transport Alliance), the association of companies using blockchain technology in supply chain.
For BiTA members, the key for this technology to be implemented successfully in their sector is to create universal standards to get rid of administrative inconsistencies and to improve the visibility of merchandise and the transparency of processes.
This year, BiTa published its first manual of standards, and it expects to grow it as issues such as chain of custody, asset maintenance, and ownership history are discussed.
The challenges faced by this technology in terms of the necessary financial investment, the adjustments of existing and applicable regulations, and the resistance to change among participants, aren’t few, but the great benefits of applying the blockchain technology to logistics will end up imposing it.
*This blog was originally published on June 10 2019 and modified on April 2 2022.







